
How did I get type 2 diabetes, and can I pass it on?
Do you want to learn more about type 2 diabetes? Read about the common misconceptions so that you can fully understand all of its causes.
If you're living with type 2 diabetes, you've probably heard a lot about managing your blood sugar levels. But what does that really mean, and when should you be concerned?
Insulin is crucial for keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range, preventing unwanted spikes and drops. Living with type 2 diabetes means the insulin your body makes becomes less effective and your pancreas, the organ that produces insulin, has to work overtime. Over months, and years, the pancreas tires and cannot keep up with the demand. Without enough insulin, sugar builds up in your blood, which can lead to health problems over time1,2.

While managing your blood sugar levels is important, with knowledge and the right treatment plan it doesn’t need to be a source of anxiety. Your healthcare professional is your first port of call for information about how to learn about and manage your blood sugar levels.
Simply put, your blood sugar level is an estimate of how much sugar is in your blood. By tracking your blood sugar level, you can identify the causes of spikes and drops which will help you manage your disease in the long term and may help avoid additional health complications3,4. There are a few different methods of testing commonly used to keep track of this:
Managing your blood sugar levels is important for feeling your best and protecting your long-term health7. With a proper treatment plan, keeping your blood sugar levels steady can help you:
Blood sugar levels can become dangerous if they fall into the following ranges:
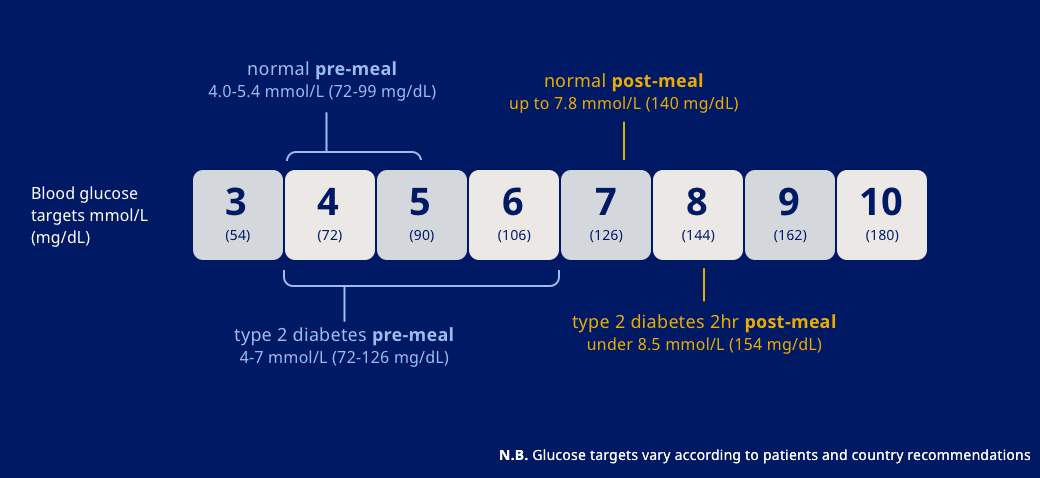
Remember, everyone's target range is different! Your healthcare team will help you figure out what's right for you.
Managing your blood sugar might seem daunting at first, but with time and practice it becomes second nature. It's all about learning to listen to your body and working with your healthcare team to find what works best for you.
Still have questions around starting insulin therapy for your type 2 diabetes? Read through our guide and take notes on questions you can ask your healthcare professional here.
HQ24DI00293